You might approach writing with a mixture of caution, excitement and dread. On one hand, you look forward to sharing sweeping tales about your ancestors, the journeys they have taken and the triumphs and trials they have faced.
On the other hand, though, writing can be downright hard. The saying goes that the pen is mightier than the sword (or, in our digital world, the laptop or other electronic device). But when you struggle to find the right words to describe a person who means a great deal to you, the pen might feel like little more than a blunt stick.
In fact, because family stories are so personal, writing about them can be harder than writing about something more scientific or technical. You may know more about Grandma Ethel and her childhood than anyone else—but you know so much that you fear you will gloss over something important. Every time you sit down to write about her, nagging thoughts arise: what if I’m not doing her story justice? What if I’m leaving out important details or homing in on the wrong details? What if I’m just not the writer for the job?
Fortunately, writing doesn’t have to feel like a long, uncertain battle. You can break the writing process down into manageable parts, turning it from stressful slog into an illuminating journey.
Creating a handy outline can help. Below are some strategies to guide you in creating an outline that covers all you want to share about your family history.
What Is a Writing Outline?
A writing outline is a tangible plan in which you lay out:
- what you are writing
- about whom or what you are writing
- the structure or organization of your work
Outlines take many different forms. Some may be linear, plotting out exactly what happens from the beginning to the end. For example, a story of your grandfather’s immigration to America may begin with the moment he left his homeland and end with him stepping foot on unfamiliar land.
Other outlines have a more stream-of-consciousness structure; you simply write whatever comes to mind as you brainstorm and use your notes as your guide. In this case, you might highlight specific descriptions or moments of your grandfather’s voyage, but don’t connect the dots, at least right away.
This article focuses mostly on structured outlines. But the “right” outline is whichever feels the most useful to you.
And whatever outline you create, nothing in it has to be set in stone. Even if you map out Grandpa’s life perfectly from its humble start to its glorious conclusion, you may decide as you write to change some parts around, to add details or to omit entire swaths of time and text altogether.
That’s okay. What makes the writing process so rewarding is uncovering old fond memories that you thought had turned to dust or making new, startling epiphanies that enliven your story.
Every time I write something new, be it a story or article or essay, I end up writing something very different than what I had initially envisioned. Even the final draft of this article looks quite different from my outline. I embrace these differences, and I also embrace my outlines for carrying me to the end.
Types of Outlines
What does an outline look like? Below I highlight several common types and provide examples of each. Your outline might look entirely different, or blend elements from several varieties. What’s important is that you find an outlining strategy that helps you write your family history the way you want.
The Alphanumeric Outline
The alphanumeric outline is exactly what it sounds like: It uses a combination of letters (lowercase or uppercase) and numbers (Arabic or Roman numerals) to denote hierarchies in your thought process.
For example, you might identify three main topics you want to highlight in your family history and number them 1, 2 and 3. Then you can expand upon a main topic with supporting, more-specific “sub-topics” that you label a, b and c under the main idea. To put it another way, the main topic serves as an “umbrella” over those sub-topics.
You’ve probably used this outline to write structured essays in school—ones with a clear introduction and thesis statement, a cohesive body and a compelling conclusion. The alphanumeric outline is ideal if you’re looking to write a chronological family history that has a clear order to your thoughts.
Below is an example of an alphanumeric outline I drafted up to write a piece on my own family history:

Note that my topics have different numbers of sub-topics beneath them. Your outline, too, might not look completely balanced. Some subjects might simply spur more inspiration or warrant a more-detailed discussion. I also gave my outline a temporary, working title to differentiate it from other outlines.
The Sentence Outline
Like the alphanumeric outline, the sentence outline sorts ideas and subjects into subject groups. However, each topic and sub-topic is written as a complete sentence. Sometimes, I’m so overflowing with ideas that I break the rules and end up creating a (short) paragraph outline.
While it may seem like extra work, this outline is useful. It forces you to engage with your ideas just as you would while writing your actual family history. As a result, you can potentially identify at the outline level what you need to expand upon and what you could possibly pare down. For instance, if you struggle to write even one sentence to sum up the topic, you may consider reworking the topic altogether.
Another thing I appreciate about the sentence outline is that it allows me to play with language and tone. Most sentences from the outline won’t survive to the actual written family history, but they do help me uncover sensory images and valuable details that I might otherwise overlook during the writing process.
I also may notice certain themes that emerge organically and tie my story together. For example, I found that the concept of myths and mythologizing the past threaded many of the topics in my outline together. This revelation helped guide my narrative throughout the entire piece.
Here’s a sentence outline for the first topic I laid out in my alphanumerical outline:

The Mind Map
If the outlines mentioned above feel too academic or rigid for you (or you just want something more visual), then the mind map may be right for you. The mind map usually begins with a single “seed” of a topic—something general, like “My Family History”—then branches off into many separate topics that intersect or sprout their own “sub-topics.” (It goes without saying, then, that a tree is an apt metaphor for the family history mind map!)
The mind map can help you visualize where your ideas are in relation to one another. As you add new ideas to your mind map, it grows, as does your understanding of what you are writing about.
Here’s a mind map outline that I created using a free version of Coggle:
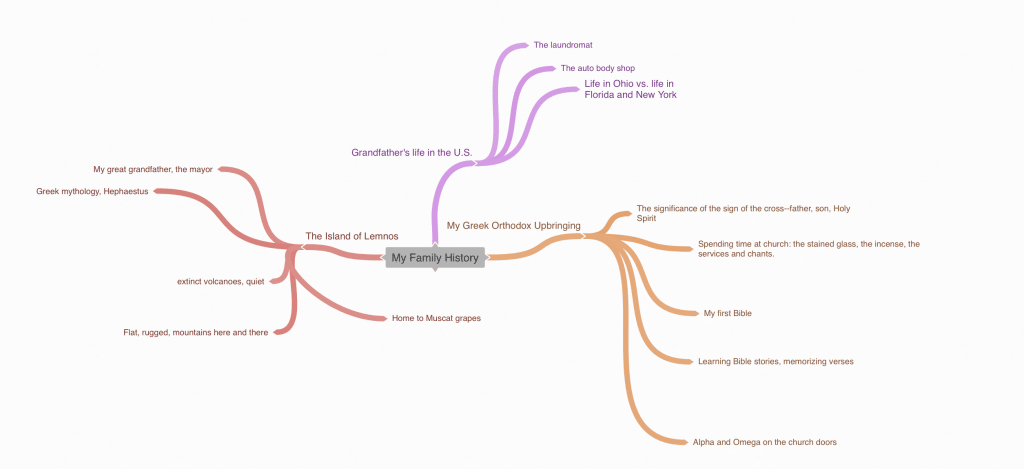
Most mind-mapping tools allow you to create several free mind maps and use basic mapping capabilities. The paid versions of these tools offer unlimited maps and more complex features (for example, color-coding, more bubble shape options, etc.).
Here’s a quick breakdown of five different mind-mapping tools: Coggle, GitMind, Microsoft Visio, MindMeister and Miro. You can review this chart for number of free maps, free features offered, paid features offers and price.
| Company | # of Free Mind Maps Offered | Free Features | Paid Features | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coggle | 3 | Unlimited public diagrams, unlimited photo uploads, change history, several start points, branch auto-arrange feature | Unlimited private mind maps, control line path, change line style, more item shape options, high resolution photo downloads | $5/month |
| GitMind | 10 | Color themes, outline mode, slideshow capabilities | Free features + unlimited mind maps, nodes, and templates | $9/month |
| Microsoft Visio | Unlimited with 1 month trial | Enjoy all features during trial period | Many different templates and shapes, cross functional flowcharts, app to work anywhere | $5/month |
| MindMeister | 3 | Outline mode, customizable text colors and styles, custom icon color | Unlimited mind maps, file and image attachments, export PDFs and image, mind map printing | $4.99/month |
| Miro | 3 | Premade templates, integration with Google Drive, Microsoft and other programs | Unlimited mind maps, custom templates, project folders, high-resolution export capabilities, board version history | $8/month |
Beyond the Outline: Family History Writing Organization Strategies
You might want jump right into writing once you’ve got an outline. By all means, go ahead! But if you’re still apprehensive, here are tips that will help you ease into the writing process, both before and after you start drafting an outline.
Before the Outline
Determine the Form and Length of Your Project
Few writers can accurately predict how many words a piece will be, so it’s okay if you’re unsure about the length of your family history. However, your outline will be more helpful if it reflects the scope of your project: how deep you plan to go into your family history and what kind of form it’s going to take.
For example, are you writing a book-length memoir that captures snapshots throughout an ancestor’s life? Or are you weaving a narrative that has a clear beginning, middle and end? Is your family history going to be a cohesive narrative, or (like mine) a collection of shorter essays or stories tied together by a theme?
Determine Who You are Going to Write About
This might go without saying, but you’ll need to know who is going to appear in your written family history before you start outlining it. With that decided, you can spend the outlining stage sketching an accurate portrait of the person(s).
Determine Where You Fit into the Story
When you read a book (especially a work of fiction), the narrative point of view is usually one of the first pieces of information you receive. Who is telling the story?
Your family history isn’t fiction, of course. But you’ll want to decide how personal your storytelling will be. Will you let readers get a closer look at who you (the author) are, through personal memories? Or will family stories be told from the point of view of an omniscient, impersonal narrator? There’s no right or wrong answer, but deciding on an approach will help you build your outline.
After the Outline
Organize and Integrate Research
Once you have your outline in hand, you can start incorporating your research into it. This is more challenging than it first seems, since you probably have decades of research and plenty of facts that you want to share. It can be tempting to dump all of that information on the page during the outline stage, but I get less overwhelmed if I write my outline first, then match details and facts to specific topics mentioned in my outline.
Make sure that the research you include is relevant to the story and reflects your overall vision. You don’t want your narrative to be bogged down in unrelated details.
Identify Common Images and Narrative Threads
I mentioned above how, during the outlining process, I recognized and embraced the theme of mythology that had emerged from my outline. As you study your own, look out for those such motifs. They might not be broad (such as connections to mythology) or subtle (such as memories of the sky, sea or birds).
Of course, you shouldn’t force such imagery into your writing if it feels unnatural. But concrete images can enrich your story and provide an emotional connection that your readers will respond to.
Find Photos, Heirlooms and Other Items That Can Help Strengthen Your Story
Consider looking through your family photos and keepsakes to find any objects that will help bring your story to life. While colorful descriptions of Grandma’s kitchen at Christmas can help readers visualize the scene (a flour-covered counter, or the smell of freshly baked cookies), an actual photo can transport them there.
For example, my Yia Yia kept a journal that dates to when I was just a baby. In it, she recorded notable milestones, stowed away some fun projects we did together and described some of our trips to church. I could describe this journal to you in great detail, but that probably wouldn’t be as interesting as seeing it for yourself!

Final Thoughts
Outlines don’t force your family history into a prescribed, write-by-number template. Instead they guide your thoughts, spark memories and move you through years of joys and sorrows. You can always deviate from your outline—you don’t have to commit to a certain topic just because your outline says so. The outline is only a foundation that you can build higher or reshape as you see fit. Keeping that in mind will leave you open to your own treasured memories: how peaceful you felt when you walked with your grandpa through the woods; the touch of his weathered hand in your own; the sound of his wise, booming voice; how his shadow disappeared into those of the trees.
Related Reads
A version of this article appeared in the May/June 2023 issue of Family Tree Magazine.










