Sign up for the Family Tree Newsletter! Plus, you’ll receive our 10 Essential Genealogy Research Forms PDF as a special thank you.
Get Your Free Genealogy Forms
"*" indicates required fields

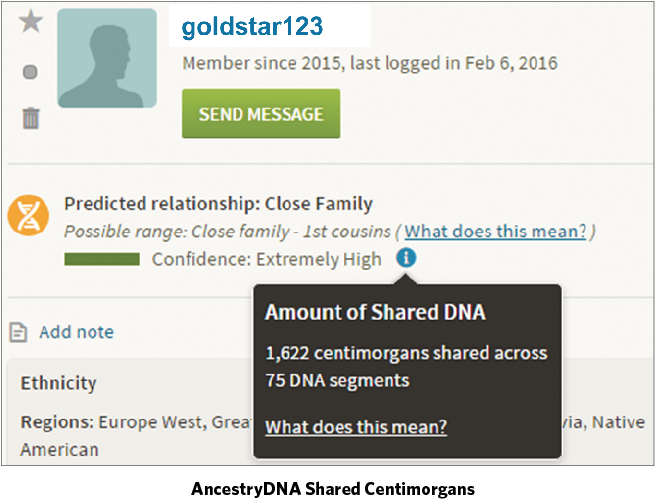
Q. I’m a 33-year-old adoptee, and I’ve tested my autosomal DNA at 23andme.com, AncestryDNA and Family Tree DNA. AncestryDNA predicts my closest match there as “Close family—first cousins.” This match and I share 1,622 centimorgans of DNA across 75 DNA segments. The person doesn’t have a family tree attached to his profile and hasn’t uploaded his results to GEDmatch. I don’t know how old he is. What’s our likely relationship?
A. A close match is the goal of most adoptees who turn to genetic genealogy testing, as this can help reveal genetic heritage. Once you’ve identified a close match, the next step is to determine the most likely genealogical relationship with that match, which will help you figure out how the match fits within the family tree that’s beginning to reveal itself.
All the testing companies now provide the total amount of DNA (measured in centimorgans, or cM) shared with each genetic match, information that can be vital for determining the genealogical relationship. A cM is a measurement of the distance between genetic markers on the DNA based on the expected frequency of recombination with each generation. On average, one cM equals one million base pairs, although this can vary.
One you know the number of shared centimorgans, your first stop for estimating a relationship is the International Society of Genetic Genealogy’s (ISOGG) Autosomal DNA Statistics page. This page contains a table summarizing the average amount of DNA (in percentages and centimorgans) shared in a wide variety of genealogical relationships. You can see it on the opposite page.
Remember that these figures are the average amount of DNA that relatives will share; thus, the actual amount of shared DNA will likely vary. About half the time, the amount of shared DNA will be more than the average, and about half the time the amount will be less than the average. Additionally, if the two relatives are related through more than one recent common ancestor, the relatives could share more DNA than expected.
According to AncestryDNA, you share 1,622 cM of DNA with your close match. The closest category on the ISOGG’s chart is “Grandparent/grandchild, aunt/uncle/niece/nephew, half-sibling,” relationships predicted to share 1,700 cM, or 25 percent of their DNA. The actual and estimated figures are close enough to be very confident that you and your match have one of these relationships, provided that you aren’t related through multiple ancestors.
Another resource you should use is the Shared cM Project, which collects information about actual ranges of shared cM for different genealogical relationships. Last year, the project gathered more than 7,500 data points related to amounts of shared DNA. It also visualizes the distributions for ranges of DNA shared by various relationships.

The “Degree 2” relationship includes Aunt/Uncle, Grandparent/Grandchild, and Half Siblings. The shared amount of 1,622 cM (shown by the black arrow on the chart) falls within the Degree 2 range, but not within any other ranges. For example, a shared amount of 600 cM would fall within the range for Degree 5 and Degree 6, giving a wider array of possible relationships.
Based on the ISOGG and Shared cM Project pages, it’s likely that your close match (a male) at AncestryDNA is one of these:
- your grandfather (at age 33, you’re unlikely to be a grandmother yourself)
- your uncle
- nephew, the son of a full sister or brother (if the nephew were the son of a half-sibling, you and he would share closer to 850 cM of DNA)
- your half-brother
Knowing the age of the match would help you decide between grandfather and uncle/nephew/half-sibling. However, if your match doesn’t provide his age and doesn’t respond to requests for additional information, AncestryDNA offers a tool you can use to further examine this relationship: Shared Matches.
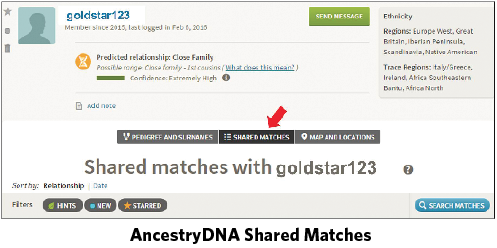
Shared Matches lets you see matches who appear on both your and your relative’s match lists. Although you can check for shared matches with anyone in your match list, you’ll see only individuals you share with that match at the fourth cousin or closer level.
If you share any matches with your relative, examine their profiles for family trees. These may provide other helpful information about this person who is likely your grandfather, uncle, nephew, or half-brother.
Related Reads
From the May/June 2016 Family Tree Magazine.